So as I said I have ton of experience. I know how to become angry mom,happy mom,super energetic mom,multi tasker mom,terrified mom and super lazy mom infact super bad mom. When you become one everyday one tag will be added in front of your name.But after everything,after every pain .I am blessed that I have became a Mom. When I hold him ,I feel lucky and everything become justified and worthy.
Automated World
Tuesday, February 14, 2023
Mom :Difficult Word but easy to pronunce
So as I said I have ton of experience. I know how to become angry mom,happy mom,super energetic mom,multi tasker mom,terrified mom and super lazy mom infact super bad mom. When you become one everyday one tag will be added in front of your name.But after everything,after every pain .I am blessed that I have became a Mom. When I hold him ,I feel lucky and everything become justified and worthy.
Thursday, December 9, 2021
Day 4: Virtual Warehouse(Part-1)
Virtual Warehouses, often referred to simply as a “warehouse”, is a cluster of compute resources in Snowflake. A warehouse provides the required resources, such as CPU, memory, and temporary storage, to perform the following operations in a Snowflake session:
- Executing SQL SELECT statements that require compute resources (e.g. retrieving rows from tables and views).
- Performing DML operations, such as
- Updating rows in tables (DELETE , INSERT , UPDATE).
- Loading data into tables (COPY INTO <table>).
- Unloading data from tables (COPY INTO <location>).
Overview of Virtual Warehouse:
Impact on Credit Usage and Billing
Impact on Data Loading
Impact on Query Processing
Auto-suspension and Auto-resumption
- By default, auto-suspend is enabled. Snowflake automatically suspends the warehouse if it is inactive for the specified period of time.
- By default, auto-resume is enabled. Snowflake automatically resumes the warehouse when any statement that requires a warehouse is submitted and the warehouse is the current warehouse for the session.
What is a Multi-cluster Warehouse?
- Maximum number of warehouses, greater than 1 (up to 10).
- Minimum number of warehouses, equal to or less than the maximum (up to 10).
- Specifying a warehouse size.
- Resizing a warehouse at any time.
- Auto-suspending a running warehouse due to inactivity; note that this does not apply to individual warehouses, but rather the entire multi-cluster warehouse.
- Auto-resuming a suspended warehouse when new queries are submitted.
Maximized vs. Auto-scale
Maximized
Auto-scale
Benefits of Multi-cluster Warehouses
- You must either increase the size of the warehouse or start additional warehouses and explicitly redirect the additional users/queries to these warehouses.
- Then, when the resources are no longer needed, to conserve credits, you must manually downsize the larger warehouse or suspend the additional warehouses.
- In Auto-scale mode, a multi-cluster warehouse eliminates the need for resizing the warehouse or starting and stopping additional warehouses to handle fluctuating workloads. Snowflake automatically starts and stops additional warehouses as needed.
- In Maximized mode, you can control the capacity of the multi-cluster warehouse by increasing or decreasing the number of warehouses as needed.
Day 3:SnowFlake's Storage Layer
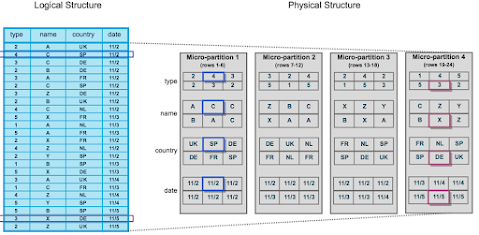
Micro-partitions & Data Clustering
What are Micro-partitions?
Snowflake stores metadata about all rows stored in a micro-partition, including:
- The range of values for each of the columns in the micro-partition.
- The number of distinct values.
- Additional properties used for both optimization and efficient query processing.
Benefits of Micro-partitioning
- In contrast to traditional static partitioning, Snowflake micro-partitions are derived automatically; they don’t need to be explicitly defined up-front or maintained by users.
- As the name suggests, micro-partitions are small in size (50 to 500 MB, before compression), which enables extremely efficient DML and fine-grained pruning for faster queries.
- Micro-partitions can overlap in their range of values, which, combined with their uniformly small size, helps prevent skew.
- Columns are stored independently within micro-partitions, often referred to as columnar storage. This enables efficient scanning of individual columns; only the columns referenced by a query are scanned.
- Columns are also compressed individually within micro-partitions. Snowflake automatically determines the most efficient compression algorithm for the columns in each micro-partition.
Impact of Micro partitions:
DML
Query Pruning
Data Clustering
Clustering Information Maintained for Micro-partitions
- The total number of micro-partitions that comprise the table.
- The number of micro-partitions containing values that overlap with each other (in a specified subset of table columns).
- The depth of the overlapping micro-partitions.
Clustering Depth
- Monitoring the clustering “health” of a large table, particularly over time as DML is performed on the table.
- Determining whether a large table would benefit from explicitly defining a clustering key.
Clustering Depth Illustrated
Example of clustering depth
- At the beginning, the range of values in all the micro-partitions overlap.
- As the number of overlapping micro-partitions decreases, the overlap depth decreases.
- When there is no overlap in the range of values across all micro-partitions, the micro-partitions are considered to be in a constant state (i.e. they cannot be improved by clustering).
Day 2:SnowFlake Architecture
Snowflake’s architecture is a hybrid of traditional shared-disk and shared-nothing database architectures. Similar to shared-disk architectures, Snowflake uses a central data repository for persisted data that is accessible from all compute nodes in the platform. But similar to shared-nothing architectures, Snowflake processes queries using MPP (massively parallel processing) compute clusters where each node in the cluster stores a portion of the entire data set locally. This approach offers the data management simplicity of a shared-disk architecture, but with the performance and scale-out benefits of a shared-nothing architecture.
Snowflake’s unique architecture consists of three key layers:
- Database Storage
- Query Processing
- Cloud Services
Database Storage
Query Processing
Cloud Services
Services managed in this layer include:
- Authentication
- Infrastructure management
- Metadata management
- Query parsing and optimization
- Access control
Understanding Snowflake Data Transfer Billing
Tuesday, December 7, 2021
Day 1: SnowFlake Overview
Snowflake’s Data Cloud is powered by an advanced data platform provided as Software-as-a-Service (SaaS). Snowflake enables data storage, processing, and analytic solutions that are faster, easier to use, and far more flexible than traditional offerings.
The Snowflake data platform is not built on any existing database technology or “big data” software platforms such as Hadoop. Instead, Snowflake combines a completely new SQL query engine with an innovative architecture natively designed for the cloud. To the user, Snowflake provides all of the functionality of an enterprise analytic database, along with many additional special features and unique capabilities.
Snowflake is a true SaaS offering. More specifically:
- There is no hardware (virtual or physical) to select, install, configure, or manage.
- There is virtually no software to install, configure, or manage.
- Ongoing maintenance, management, upgrades, and tuning are handled by Snowflake.
- Snowflake runs completely on cloud infrastructure. All components of Snowflake’s service (other than optional command line clients, drivers, and connectors), run in public cloud infrastructures.
- Snowflake uses virtual compute instances for its compute needs and a storage service for persistent storage of data. Snowflake cannot be run on private cloud infrastructures (on-premises or hosted).
- Snowflake is not a packaged software offering that can be installed by a user. Snowflake manages all aspects of software installation and updates.
Six Features That Make Snowflake A Different Cloud Data Warehouse:
Cloud Provider Agnostic
Snowflake is a cloud agnostic solution. It is a managed data warehouse solution that is available on all three cloud providers: AWS, Azure and GCP, while retaining the same end user experience. Customers can easily fit Snowflake into their current cloud architecture and have options to deploy in regions that makes sense for the business.
Scalability
Snowflakes multi-cluster shared data architecture separates out the compute and storage resources. This strategy enables users the ability to scale up resources when they need large amounts of data to be loaded faster, and scale back down when the process is finished without any interruption to service. Customers can start with an extra-small virtual warehouse and scale up and down as needed.
To ensure minimal administration, Snowflake has implemented auto-scaling and auto suspend features. Auto-scaling enables Snowflake to automatically start and stop clusters during unpredictable resource intensive processing. Auto-suspend, on the other hand, stops the virtual warehouse when clusters have been sitting idle for a defined period. These two concepts provide flexibility, performance optimization, as well as cost management.

Concurrency and Workload Separation
In a traditional data warehouse solution, users and processes would compete for resources resulting in concurrency issues. Hence the need for running ETL/ELT jobs in the middle of the night when no one is running reports. With Snowflake’s multi-cluster architecture, concurrency is no longer an issue. One of the key benefits of this architecture is separating out workloads to be executed against its own compute clusters called a virtual warehouse. Queries from one virtual warehouse will never affect queries from another. Having dedicated virtual warehouses to users and applications provides the possibility to run ETL/ELT processing, data analysis operations and reports without competing for resources.
Near-Zero Administration
Snowflake is delivered as a Data Warehouse as a service (DWaas). It enables companies to setup and manage a solution without significant involvement from DBA or IT teams. It does not require software to be installed or hardware to be commissioned. With modern features such as auto scaling, both increasing the virtual warehouse size as well as increasing clusters, gone are the days for server size and cluster management. Since Snowflake supports no indexes there is no need for tuning the database or indexing the tables. Software updates are handled by Snowflake and new features and patches are deployed with zero downtime.
Semi-Structured Data
The rise of NoSQL database solutions came from a need to handle semi structured data, typically in JSON format. To parse JSON, data pipelines needed to be developed to extract attributes and combine those attributes with structured data. Snowflake’s architecture allows the storage of structured and semi structured data in the same destination by utilizing a schema on read data type called VARIANT. The VARIANT data type can store both structured and semi structured data. As data gets loaded, Snowflake automatically parses the data and extracts the attributes and stores it in a columnar format. Hence eliminating the need for data extraction pipelines.
Security
From the way users access Snowflake to how data is stored, Snowflake has a wide array of security features. You can manage network polices by whitelisting IP addresses to restrict access to your account. Snowflake supports various authentication methods including two-factor authentication and support for SSO through federated authentication. Access to objects in the account is controlled through a hybrid model of discretionary access control (each object has an owner who grants access to the object) and role-based access control (privileges assigned to roles which are then assigned to users). This hybrid approach provides significant amount of control and flexibility. All data is automatically encrypted using AES 256 strong encryption and is encrypted in transit as well as at rest.
These are not the only reasons why Snowflake is different. There are other features that standout, however these are the ones we have seen our clients benefit from the most. Snowflake should be considered as a solution for any business migrating to a cloud Data Warehouse. One Six Solutions is a Snowflake partner and has implemented Snowflake Cloud Data Platform solutions for clients looking for a modern data architecture platform.
Friday, April 5, 2019
How to use Apache Drill
- Get started in
minutes:It takes just a few minutes to get started with Drill.
- Schema-free JSON
model:No need to define and maintain schemas or transform data (ETL).
Drill automatically understands the structure of the data.
- Query complex,
semi-structured data in-situ:Using Drill's schema-free JSON model, you can
query complex, semi-structured data in situ. No need to flatten or
transform the data prior to or during query execution.
- Leverage
standard BI tools:Drill works with standard BI tools. You can use your
existing tools, such as Tableau,
- Access multiple
data sources:You can connect Drill out-of-the-box to file systems (local
or distributed, such as S3 and HDFS), HBase and Hive
- High
performance:Drill is designed from the ground up for high throughput and
low latency. It doesn't use a general purpose execution engine like
MapReduce, Tez or Spark. As a result, Drill is flexible (schema-free JSON
model) and performant.






- RPC endpoint:
Drill exposes a low overhead protobuf-based RPC protocol to communicate
with the clients.
- SQL parser:
Drill uses Calcite, the open source SQL parser
framework, to parse incoming queries. The output of the parser component
is a language agnostic, computer-friendly logical plan that represents the
query.
- Storage plugin interface: Drill serves as a query layer on
top of several data sources.In the context of Hadoop, Drill provides
storage plugins for distributed files and HBase. Drill also integrates
with Hive using a storage plugin.
- Embedded
mode:./sqlline -u jdbc:drill:drillbit=local
- Distributed
mode:./sqlline –u jdbc:drill:zk=cento23,centos24,centos26:2181
You can create your own workspace in drill. Workspace is nothing but the directory in which you can create your views / tables. You can define one or more workspaces in a storage plugin configuration.

- workspace:The
location where you want the view to exist. By default, the view is created
in the current workspace.
- view_name:The
name that you give the view. The view must have a unique name. It cannot
have the same name as any other view or table in the workspace.
- column_name:Optional
list of column names in the view. If you do not supply column names, they
are derived from the query.
- query:A SELECT
statement that defines the columns and rows in the view.

- Select the
workspace by command use dfs.supply_view;
- Create view
dummy as select * from hive.`default`.employee.


Use this URL when HTTPS support is disabled (the default).
https://<IP address or host name>:8047
Use this URL when HTTPS support is enabled.
http://localhost:8047
Use this URL when running Drill in embedded mode (./drill-embedded).


Mom :Difficult Word but easy to pronunce
Hi bloggers ,I know this is not good post to read but i know you will all relate with this emotion. When you around with your Mom,you feel s...
-
Traditionally data warehouses take too long to build and are too hard to change. WhereScape RED is an Integrated Development Environment...
-
Hi bloggers ,I know this is not good post to read but i know you will all relate with this emotion. When you around with your Mom,you feel s...
-
Drill is an Apache open-source SQL query engine for Big Data exploration. Drill is designed to support high-performance analysis on the s...